Power Calculators
➤ Calculate Current in Amperes from Kilo Volt Amperes (KVA)
➤ Calculate Kilo Watts (KW) from Kilo Volt Amperes (KVA)
➤ Calculate Kilo Volt Amperes (KVA) from Kilo Watts (KW)
➤ Calculate HorsePower from Kilo Watts (KW)
➤ Calculate Kilo Volt Amperes (KVA) from HorsePower
Calculate Current in Amperes from Kilo Volt Amperes (KVA)
Calculate Kilo Watts (KW) from Kilo Volt Amperes (KVA)
Calculate Kilo Volt Amperes (KVA) from Kilo Watts (KW)
Calculate HorsePower from Kilo Watts (KW)
Calculate Kilo Volt Amperes (KVA) from HorsePower
What is a Power Calculator?
A Power Calculator is a tool used to calculate various aspects of electrical power in circuits. These calculators help in determining values like power consumption, power dissipation, or power output based on other known parameters, such as voltage, current, resistance, and efficiency. Power calculators can be used for a variety of purposes, including sizing components, analyzing energy efficiency, or ensuring that circuits meet safety and performance requirements.
Why are Power Calculators needed?
Power calculators are essential for several reasons:
- Circuit Design: They help designers calculate the power requirements of components and circuits to ensure proper operation and avoid overloading.
- Component Selection: By knowing the required power for a circuit, designers can select components (resistors, capacitors, transistors, etc.) that can safely handle that power.
- Energy Efficiency: Power calculators help assess how much energy is consumed by circuits or devices, which is essential for optimizing performance and improving energy efficiency.
- Safety: Overpowering components can lead to overheating or failure. Using power calculators ensures that circuits stay within safe operating limits.
- Cost Estimation: For large-scale systems, such as power grids or data centers, power calculators help estimate electricity usage, which is crucial for cost management.
How do Power Calculators work?
Power calculators typically use fundamental electrical formulas to calculate power. The basic formula for power in an electrical circuit is:
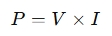
Where:
- P = Power (in watts, W)
- V = Voltage (in volts, V)
- I = Current (in amperes, A)
For resistive circuits, the power can also be calculated using Ohm’s Law:
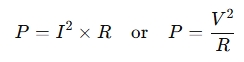
Where:
- R = Resistance (in ohms, Ω)
In AC circuits, especially with alternating current (AC), power calculations may need to account for the power factor (pf), which adjusts the real power consumed:
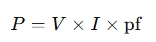
The calculator may also include parameters like efficiency (η) for devices such as motors:
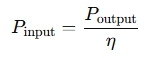
When should Power Calculators be used?
Power calculators should be used in the following situations:
-
During Circuit Design:
When designing electrical circuits, power calculators help ensure that components can handle the required power levels. For example, when selecting resistors, capacitors, or power supplies, you need to know how much power will be dissipated in the circuit. -
Component Sizing:
Before purchasing or assembling components, power calculators are used to determine the power ratings required. For example, determining the power rating of resistors or fuses ensures that they won't overheat or fail. -
Optimizing Energy Efficiency:
Power calculators are useful for evaluating the energy efficiency of devices or systems, allowing engineers to optimize designs for lower power consumption, which is important in applications like mobile devices, renewable energy systems, or low-power electronics. -
Verifying Power Consumption:
Power calculators can be used to verify that a system's power consumption is within safe limits, ensuring that circuits are operating at optimal performance levels without drawing excessive power that could lead to inefficiencies or failures. -
Troubleshooting:
If a circuit isn't working as expected, you can use a power calculator to verify that the power supplied is within the required range for all components, which can help in diagnosing issues like power supply failure or component overload.
Types of Power Calculators
- DC Power Calculators: Used for direct current (DC) circuits, often involving battery-powered devices or simpler circuits.
- AC Power Calculators: For alternating current (AC) circuits, especially in power distribution systems, home appliances, or industrial machinery, where phase differences and power factors must be considered.
- Power Dissipation Calculators: Used to calculate how much power is lost as heat in components like resistors or transistors.
- Energy Consumption Calculators: Used to estimate the total energy consumption over time, typically measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), which is useful for estimating electricity costs.


Search for Calculator
Explore thousands of free calculators trusted by millions worldwide.