Specific Heat and Density Calculator
Select the material from the drop down box below. Result will be displayed.
What is a Specific Heat and Density Calculator?
A Specific Heat and Density Calculator is a tool used to determine:
- Specific Heat Capacity (Cp) – the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 kg of a substance by 1°C (or 1 K).
- Density (ρ) – the mass per unit volume of a substance, used in material science and fluid dynamics.
These properties are crucial in thermodynamics, engineering, chemistry, and industrial applications.
Specific Heat Formula:
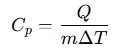
where:
- Cp= Specific heat capacity (J/kg·K)
- Q= Heat energy (Joules)
- m= Mass (kg)
- ΔT= Temperature change (°C or K)
Density Formula:
ρ=m/Vwhere:
- ρ= Density (kg/m³)
- m= Mass (kg)
- V= Volume (m³)
Why Use a Specific Heat and Density Calculator?
- Energy Efficiency: Helps determine how much energy is required to heat or cool a material.
- Material Selection: Engineers choose materials based on their density and heat capacity for construction, insulation, and manufacturing.
- Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulics: Density is essential for calculations in fluid dynamics, buoyancy, and pressure analysis.
- HVAC & Refrigeration: Used to optimize heating/cooling systems in buildings and industrial processes.
- Chemical & Pharmaceutical Processing: Helps in controlling temperature-sensitive reactions and processes.
How Does a Specific Heat and Density Calculator Work?
-
Inputs Required:
- Mass (m) and Volume (V) for density calculation.
- Heat energy (Q), mass (m), and temperature change (ΔT) for specific heat calculation.
-
Processing:
- Uses the given formulas to compute specific heat capacity (Cp) and density (ρ).
-
Outputs:
- Specific Heat Capacity in J/kg·K.
- Density in kg/m³.
When to Use a Specific Heat and Density Calculator?
- In Thermal Engineering: To design efficient heating and cooling systems.
- In Aerospace & Automotive: To optimize fuel efficiency and heat dissipation.
- In Civil Engineering & Construction: To select materials with ideal thermal properties.
- In Chemical & Food Industry: To control thermal processes and ensure safety.
- In Academic Research & Laboratory Work: For physics, chemistry, and engineering experiments.
Did this Calculator help you?
Thanks for the feedback


Search for Calculator
Explore thousands of free calculators trusted by millions worldwide.