Standard Temperature and Pressure Calculator
Enter value and click on calculate. Result will be displayed.
What is a Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP) Calculator?
A Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP) Calculator is a tool used to convert gas volumes, pressures, and temperatures based on standard reference conditions. These conditions help in comparing gas properties across different experiments and industrial processes.
Standard Conditions for STP
Different organizations define STP slightly differently, but the most common definitions are:
| Organization | Temperature (°C) | Temperature (K) | Pressure (atm) | Pressure (Pa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC (Current) | 0°C | 273.15 K | 1 atm | 101,325 Pa |
| NIST (Older Definition) | 25°C | 298.15 K | 1 atm | 101,325 Pa |
Why Use an STP Calculator?
- Gas Volume Comparisons: Since gases expand and contract with temperature and pressure, STP provides a consistent reference.
- Ideal Gas Law Applications: Used in chemistry, physics, and engineering for gas calculations.
- Scientific & Industrial Processes: Helps standardize conditions in laboratories, manufacturing, and environmental studies.
- Aviation & Meteorology: Used to calculate air densities and atmospheric conditions.
How Does an STP Calculator Work?
-
Input Required:
- Initial pressure (P1)
- Initial temperature (T1)
- Initial volume (V1)
- Desired standard condition (IUPAC, NIST, or custom)
-
Processing:
- Uses the Ideal Gas Law and Combined Gas Law to calculate the equivalent volume at STP:
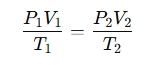
Where:- P1,V1,T1 are initial conditions.
- P2,V2,T2 are STP conditions.
- Solve for V2(volume at STP):
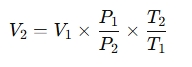
- Uses the Ideal Gas Law and Combined Gas Law to calculate the equivalent volume at STP:
-
Output:
- Volume at STP in liters or cubic meters.
When to Use an STP Calculator?
- In Chemistry & Physics: To compare gas volumes in reactions.
- In Gas Industry & Engineering: For calculating gas storage and flow rates.
- In Environmental Science: To measure air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
- In Meteorology: To adjust atmospheric data for standard conditions.
Did this Calculator help you?
Thanks for the feedback


Search for Calculator
Explore thousands of free calculators trusted by millions worldwide.