Voltage Divider Calculator
Enter any three of the following values and then click calculate button.
What is a Voltage Divider Calculator?
A Voltage Divider Calculator is a tool used to determine the output voltage in a voltage divider circuit. A voltage divider consists of two resistors connected in series across a voltage source. It divides the input voltage into smaller voltages based on the resistor values, providing a useful method for obtaining specific voltage levels in a circuit.
Why Use a Voltage Divider Calculator?
- Determine Specific Voltages – It allows you to easily calculate the output voltage across one of the resistors in a voltage divider.
- Design Circuits Efficiently – Helps design circuits that require specific voltage levels without needing complex circuitry.
- Signal Conditioning – Commonly used for signal conditioning in sensor circuits, where the input voltage needs to be scaled down for other parts of the system.
- Adjusting Impedance – Can be used to match impedance levels in different components of a circuit.
- Testing Components – Helps simulate the voltage behavior of a circuit with different resistor values.
How Does a Voltage Divider Calculator Work?
The voltage divider works on the principle that the total voltage is divided proportionally across the resistors based on their resistance values. The formula for the output voltage (V_out) in a simple voltage divider is:
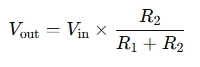
Where:
- Vin = Input voltage (Volts)
- R₁= The resistance of the first resistor (Ohms)
- R₂ = The resistance of the second resistor (Ohms)
- Vout= Output voltage (Volts)
The formula calculates the voltage drop across resistor R2, which is the output voltage in the divider.
For Example:
If you have a 12V input, with resistors R1 = 10kΩ and R2 = 10kΩ, the output voltage would be:
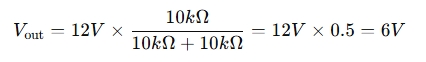
When to Use a Voltage Divider Calculator?
- Designing Sensor Circuits – When you need to scale down a voltage from a sensor to a lower, usable value for a microcontroller or another circuit.
- Adjusting Voltage Levels – If you need to reduce a voltage level in a circuit for safety or to match the required input for other components (like LEDs or analog-to-digital converters).
- Creating Biasing Networks – In transistor and op-amp circuits, where a specific voltage bias is required to operate the components correctly.
- Testing Voltage Drops – When evaluating how voltage behaves across various resistors, such as for troubleshooting or optimizing designs.
- Low-Power Designs – When designing circuits that operate at low power and need exact voltage levels without using complex regulators.


Search for Calculator
Explore thousands of free calculators trusted by millions worldwide.