BJT Transistor Bias Voltage Calculator
Enter value and click on calculate. Result will be displayed.
What is a BJT Transistor Bias Voltage Calculator?
A BJT Transistor Bias Voltage Calculator is a tool used to determine the necessary biasing voltages and currents for a Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT) to operate in a desired mode (active, cutoff, or saturation).
Why Use a BJT Bias Voltage Calculator?
- Ensures Proper Transistor Operation: Helps set the transistor in the correct region (active, saturation, or cutoff).
- Prevents Distortion & Instability: Biasing prevents unwanted shifts in performance due to temperature changes or component variations.
- Optimizes Circuit Design: Helps calculate resistors and voltage sources for stable and efficient transistor performance.
- Used in Amplifiers, Switches & Oscillators: BJT circuits are common in analog electronics, radio-frequency circuits, and switching applications.
How Does a BJT Bias Voltage Calculator Work?
-
Input Required:
- Power Supply Voltage (VCC)
- Base Resistor (RB)
- Collector Resistor (RC)
- Emitter Resistor (RE) (if present)
- Transistor Gain (β)
- Desired Operating Point (VCE , IC , etc.)
-
Processing:
- Uses Ohm’s Law and BJT Biasing Equations to compute voltages and currents.
- Example for voltage divider biasing:
- Base Voltage:
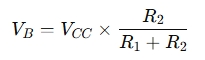
- Emitter Voltage:
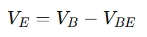
- Collector Voltage:
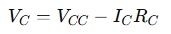
- Collector-Emitter
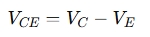
- Base Voltage:
-
Output:
- Base Voltage (VB)
- Emitter Voltage (VE)
- Collector Voltage (VC)
- Collector-Emitter Voltage (VCE)
- Collector Current (IC)
When to Use a BJT Bias Voltage Calculator?
- In Amplifier Design: Ensures stable operation for audio and RF amplifiers.
- For Switches & Digital Circuits: Helps design BJTs for on/off switching applications.
- In Power Electronics: Determines biasing for power BJTs in high-power applications.
- For Circuit Troubleshooting & Optimization: Helps diagnose incorrect biasing and improve circuit performance.
Did this Calculator help you?
Thanks for the feedback


Search for Calculator
Explore thousands of free calculators trusted by millions worldwide.